Burundi
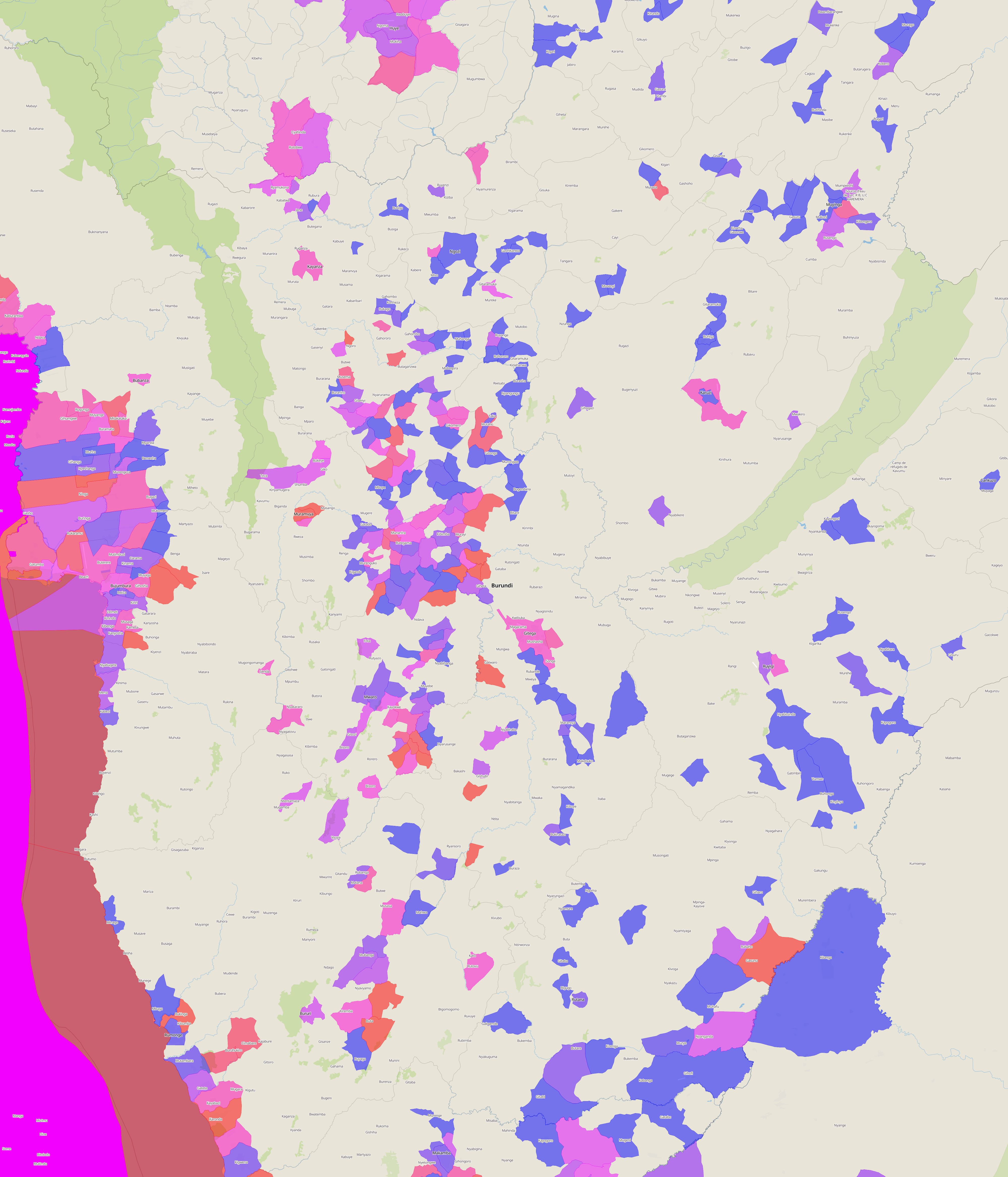
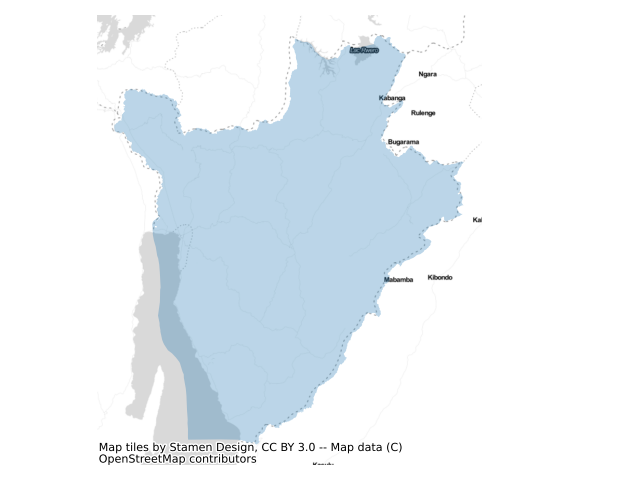
What exactly constitutes the spatial extent of the city? For these aggregations, we used the Global Human Settlement Layer Urban Center Database (GHS-UCDB) to define the boundaries of the city. These cities -- or urban centers -- cover areas that are densely populated and built-up, and so may extend beyond the spatial borders of these cities that we may be familiar with. The GHS area is shaded in blue.
View Burundi on the sprawlmap
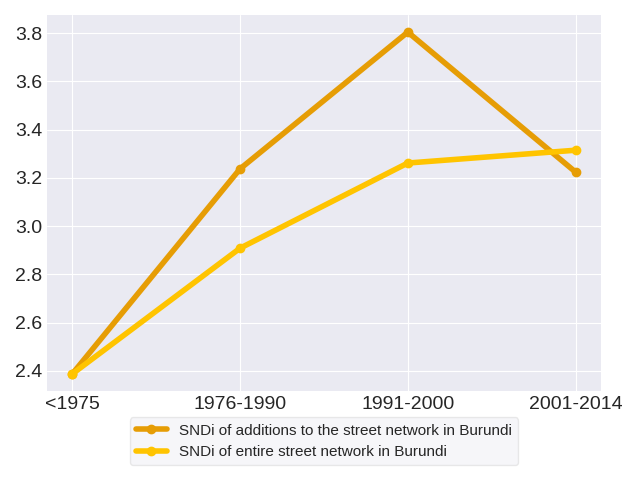
Most recent snapshot: Taking into account the entire (i.e. aggregate) street network in Burundi as of 2014, the overall level of street-network sprawl is 3.31, which is highly disconnected.
Trends in street network construction: The SNDis of street construction for the respective time periods are 2.39, 3.24, 3.8 and 3.22. Street construction in Burundi increased in disconnectivity initially but has since improved. The streets constructed in 1991-2000 were the most disconnected.
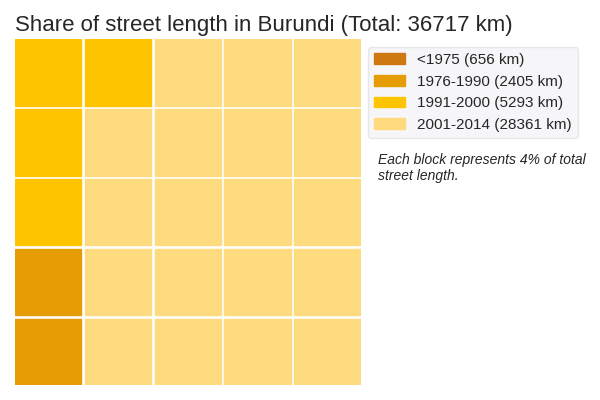
Quantity of street network construction: The street network in Burundi spans a total of 36717 kilometers. It is dominated by roads constructed in 2001-2014. These roads have an SNDi of 3.22, which is in the 40th to 60th percentile of disconnectedness.
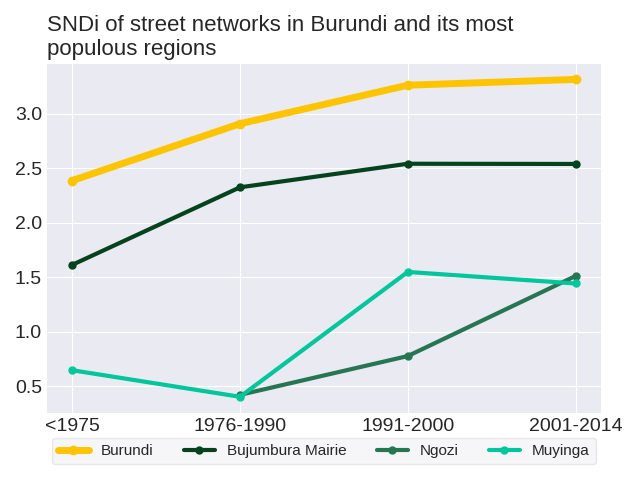
Effect on the aggregate network: New construction in each period adds to the total stock of streets, but does not change streets that have already been built. Therefore, it has a limited effect on the street network as a whole. The SNDis of the aggregate street network in the respective time periods are 2.39, 2.91, 3.26 and 3.31. Overall, the SNDi of the aggregate street network has risen: the street network in Burundi has become more disconnected. This increase has slowed: between 1975 and 1976-1990, SNDi rose by 0.52 points, but between 1991-2000 and 2001-2014, it rose by just 0.05.
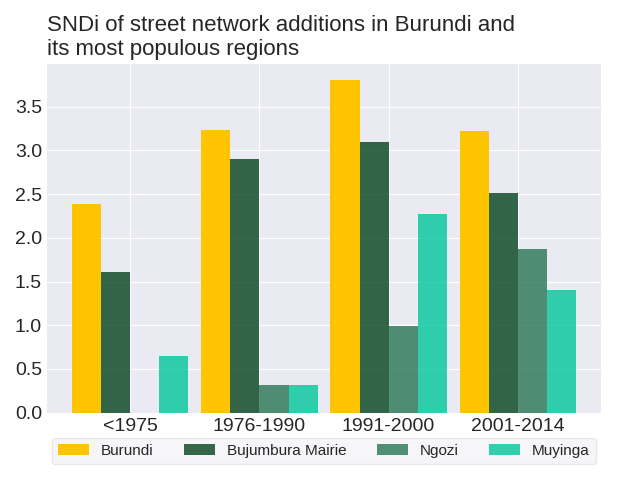
The level of street-network sprawl in new development in Burundi peaked in 1991-2000. To get a sense of how street development has changed in Burundi, we can consider three of its most populous regions: Bujumbura Mairie, Ngozi and Muyinga. Out of the three regions, Ngozi and Muyinga do not follow the same trend as the country. The level of street-network sprawl in new development in Ngozi followed a zig-zag trend. The level of street-network sprawl in new development in Muyinga followed a zig-zag trend with an overall increase.
How do development practices in Burundi fare in comparison to others in the world? Most recently in 2001-2014, street construction in Burundi was the 120th-most disconnected out of the 155 countries in the world. Its position in the ranks since 1975 has fallen; relative to other countries in the world, street construction in Burundi has become more connected. Burundi ranked 98th in 1975, 77th in 1976-1990, 92nd in 1991-2000 and 120th in 2001-2014.
The largest city in Burundi is Bujumbura, with a population of 901400 people. Taking into account the entire (i.e. aggregate) street network in Bujumbura as of 2014, the overall level of street-network sprawl is 2.52, which is in the 40th to 60th percentile of disconnectedness. The level of street-network sprawl in new development in Bujumbura peaked in 1991-2000.
As of 2014, the city with the most disconnected street network in Burundi is Muramvya with an SNDi of 6.68, which is highly disconnected. Conversely, the most connected city is Mutoyi with an SNDi of -1.33, which is very well-connected. See trends for these cities: Mutoyi, Muramvya
The level of street-network sprawl in the aggregate network in Burundi rose steadily. To get a sense of how the aggregate street network has changed in Burundi, we can consider three of its most populous regions: Bujumbura Mairie, Ngozi and Muyinga. None of the most populous cities follow the same trend as the region. The level of street-network sprawl in the aggregate network in Bujumbura Mairie peaked in 1991-2000. The level of street-network sprawl in the aggregate network in Ngozi followed a zig-zag trend. The level of street-network sprawl in the aggregate network in Muyinga followed a zig-zag trend with an overall increase.
To date, Burundi is the 82nd-most disconnected out of the 155 countries in the world. Its position in the ranks since 1975 has risen; relative to other countries in the world, the street network in Burundi has become more disconnected. Burundi ranked 98th in 1975, 88th in 1976-1990, 78th in 1991-2000 and 82nd in 2001-2014.
The largest city in Burundi is Bujumbura, with a population of 901400 people. Taking into account the entire (i.e. aggregate) street network in Bujumbura as of 2014, the overall level of street-network sprawl is 2.52, which is in the 40th to 60th percentile of disconnectedness. The level of street-network sprawl in the aggregate network in Bujumbura rose steadily.